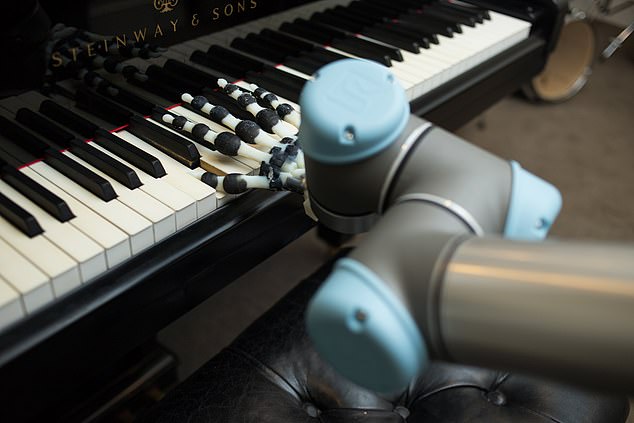
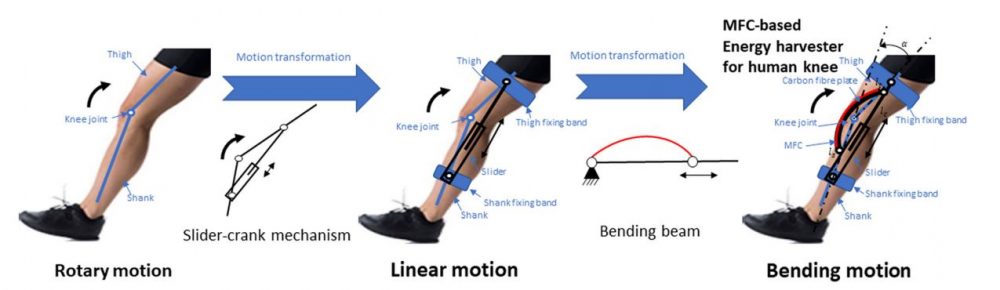
The robot hand, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, was made by 3D-printing soft and rigid materials together to replicate of all the bones and ligaments – but not the muscles or tendons – in a human hand. Even though this limited the robot hand’s range of motion compared to a human hand, the researchers found that a surprisingly wide range of movement was still possible by relying on the hand’s mechanical design.
Using this ‘passive’ movement – in which the fingers cannot move independently – the robot was able to mimic different styles of piano playing without changing the material or mechanical properties of the hand. The results, reported in the journal Science Robotics, could help inform the design of robots that are capable of more natural movement with minimal energy use.
Complex movement in animals and machines results from the interplay between the brain (or controller), the environment and the mechanical body. The mechanical properties and design of systems are important for intelligent functioning, and help both animals and machines to move in complex ways without expending unnecessary amounts of energy.
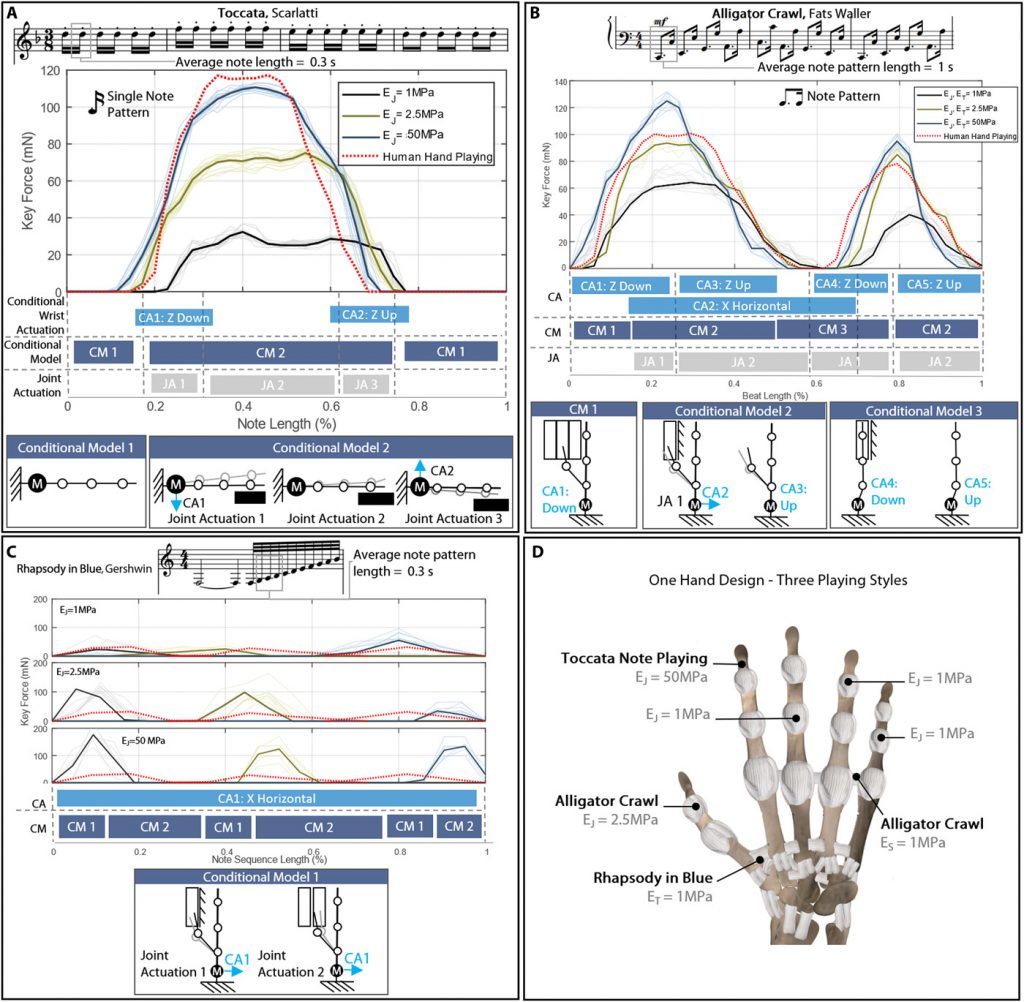
The robot was ‘taught’ to play by considering how the mechanics, material properties, environment and wrist actuation all affect the dynamic model of the hand. By actuating the wrist, it is possible to choose how the hand interacts with the piano, allowing the embodied intelligence of the hand to determine how it interacts with the environment.
The researchers programmed the robot to play a number of short musical phrases with clipped (staccato) or smooth (legato) notes, achieved through the movement of the wrist. “It’s just the basics at this point, but even with this single movement, we can still get quite complex and nuanced behaviour,” said Hughes.
The original article;
http://robotics.sciencemag.org/content/3/25/eaau3098.full